Addition of Zn to the ternary Mg–Ca–Sr alloys significantly improves their antibacterial properties
Abstract
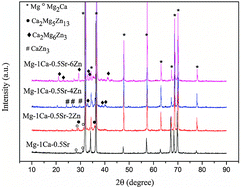
Most of the magnesium (Mg) alloys possess excellent biocompatibility, mechanical properties and biodegradability in orthopedic applications. However, these alloys may suffer from bacterial infections due to their insufficient antibacterial capability. In order to reduce the post-surgical infections, a series of biocompatible Mg–1Ca–0.5Sr–xZn (x = 0, 2, 4, 6) alloys were fabricated with the addition of antibacterial Zn with variable contents and evaluated in terms of their biocompatibility and antibacterial properties. The in vitro corrosion study showed that Mg–1Ca–0.5Sr–6Zn alloys exhibited a higher hydrogen evolution volume after 100 h immersion and resulted in a higher pH value of the immersion solution. Our work indicated that Zn-containing Mg alloys exhibited good biocompatibility with high cell viability. The antibacterial studies reveal that the number of bacteria adhered on all of these Mg alloy samples diminished remarkably compared to the Ti–6Al–4V control group. We also found that the proliferation of the bacteria was inhibited by these Mg alloy extracts. Among the prepared alloys, the Mg–1Ca–0.5Sr–6Zn alloy not only exhibited a strong antibacterial effect, but also promoted the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts, suggesting that it is a promising alloy with both good antibacterial properties and good biocompatibility for use as an orthopedic implant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...