Electrochemical deposition to construct a nature inspired multilayer chitosan/layered double hydroxides hybrid gel for stimuli responsive release of protein†
Abstract
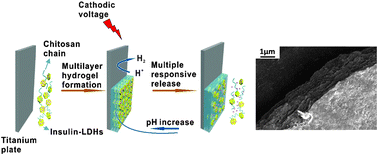
In this study, we report a single electrodeposition process to fabricate multilayered chitosan/layered double hydroxides (LDHs) hybrid hydrogels for stimuli responsive protein release. LDHs nanoplatelets with a regular hexagonal shape were synthesized by a hydrothermal method, and a model protein, insulin, was adsorbed on the surface of the LDHs (INS-LDHs) via electrostatic interactions. The insulin loading ratio could reach 20% (w/w); the INS-LDHs were characterized by energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and zeta potential measurements. Co-electrodeposition of chitosan and INS-LDHs generated an inorganic and organic composite hydrogel with a multilayered structure, as revealed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The hybrid hydrogel dramatically reduced the burst release of insulin from INS-LDHs. Notably, the release of insulin was sensitive to the presence of anions, pH, and external potentials. These results suggest that co-electrodeposition of a stimuli-responsive polymer and nanoplatelets is an alternative and facile method to construct hierarchically structured hybrid hydrogels and demonstrate the great potential of the multilayered structure in drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...