Cationic surface modification of gold nanoparticles for enhanced cellular uptake and X-ray radiation therapy†
Abstract
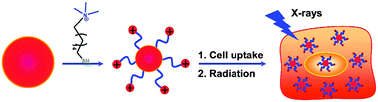
A challenge of X-ray radiation therapy is that high dose X-ray can damage normal cells and cause side effects. This paper describes a new nanoparticle-based method to reduce X-ray dose in radiation therapy by internalization of gold nanoparticles that are modified with cationic molecules into cancer cells. A cationic thiol molecule is synthesized and used to modify gold nanoparticles in a one-step reaction. The modified nanoparticles can penetrate cell membranes at high yield. By bringing radio-sensitized gold nanoparticles closer to nuclei where DNA is stored, the total X-ray dose needed to kill cancer cells has been reduced. The simulation of X-ray–gold nanoparticle interaction also indicates that Auger electrons contribute more than photoelectrons.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...