Fetuin-A adsorption and stabilization of calcium carbonate nanoparticles in a simulated body fluid†
Abstract
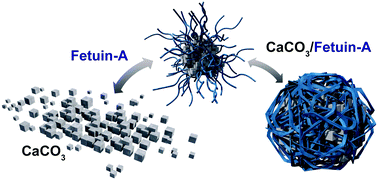
Fetuin-A is a serum glycoprotein identified as a calcification inhibitor, and a key player in bone formation and human metabolic processes. A study on binding mechanisms of Fetuin-A with calcium carbonate nanoparticles in a simulated body fluid (DMEM) environment is presented. Observed interactions between Fetuin-A and the CaCO3 nanoparticles reveal an initial adsorption process, followed by a stabilization stage, and then a solubilization period for the Fetuin-A/CaCO3 complex. FTIR and XPS are used to monitor functional group and elemental composition changes during the initial adsorption process between Fetuin-A and the CaCO3 nanoparticles. Distinctive Fetuin-A/CaCO3 complex structures—also known as mineralo-protein particles—are imaged with TEM and SEM. DLS and UV-Vis methods are used to further characterize the in situ binding mechanisms. Results of this study can guide the design of complex organic–inorganic hybrid materials, improve current drug delivery methods, and provide insight in monitoring and controlling interactions between Fetuin-A and external calcium ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...