Carbon nanotube uptake changes the biomechanical properties of human lung epithelial cells in a time-dependent manner†
Abstract
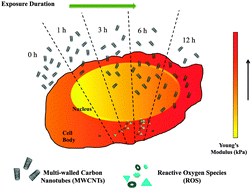
The toxicity of engineered nanomaterials in biological systems depends on both the nanomaterial's properties and the exposure duration. Herein we used a multi-tier strategy to investigate the relationship between user-characterized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) exposure duration and their induced biochemical and biomechanical effects on model human lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Our results showed that exposure to MWCNTs leads to time-dependent intracellular uptake and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), along with time-dependent gradual changes in cellular biomechanical properties. In particular, the amount of internalized MWCNTs followed a sigmoidal curve with the majority of the MWCNTs being internalized within 6 h of exposure; further, the sigmoidal uptake correlated with the changes in the oxidative levels and cellular biomechanical properties respectively. Our study provides new insights into the time-dependent induced toxicity caused by exposure to occupationally relevant doses of MWCNTs and could potentially help establish bases for early risk assessments of other nanomaterials' toxicological profiles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...