Design of multi-functional linear polymers that capture and neutralize a toxic peptide: a comparison with cross-linked nanoparticles†
Abstract
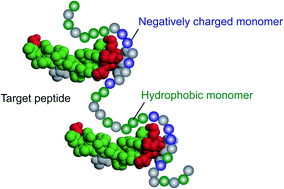
In this paper, a library of multi-functional linear poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAm) polymers having a range of molecular weights and functional groups were synthesized and their interaction with the hemolytic peptide, melittin, was examined. The linear pNIPAm (LPs) containing both tert-butyl group and carboxylic acids bound with the peptide by a combination of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions and neutralized its toxicity. The melittin binding capacity and affinity of each LP was quantified and further compared with cross-linked multi-functional nanogel particles (NPs) having same combination of functional groups. The binding capacity of the LPs (weight of captured melittin/weight of LP) was independent of their molecular weight and was three times higher than that of previously reported NPs. The binding constant depended on the molecular weight of the LPs, showing the highest value of 1.1 × 108 (M−1) for a ∼1000 mer linear polymer with 40% tert-butyl group and 20% carboxylic acid. Comparison of the interactions of the LPs and NPs suggested the importance of the flexibility of the polymer chain in order to achieve high binding capacity and affinity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...