Conjugated polymer microparticles for selective cancer cell image-guided photothermal therapy†
Abstract
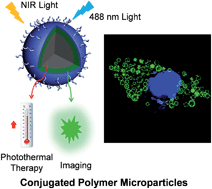
Nanotechnology has recently attracted great attention in biomedical research. Current nanoparticle approaches generally require further surface decoration with targeting ligands, peptides or proteins to achieve selective cancer imaging and therapy. This surface functionalization often complicates nanoparticles and leads to protein corona or varied nanoparticle uptake. In this work, we report a facile approach for selective cancer cell image-guided photothermal therapy by fabricating theranostic microparticles (MPs) using conjugated polymers (CPs) as the imaging and therapeutic agents. Through fine tuning of the backbone structures, we synthesized two CPs, poly[9,9-bis(4-(2-ethylhexyl)phenyl)fluorene-alt-co-6,7-bis(4-(hexyloxy)phenyl)-4,9-di(thiophen-2-yl)-thiadiazoloquinoxaline] (PFTTQ) with high near infrared (NIR) molar absorptivity and poly(9,9-dihexylfluorene-alt-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole) (PFBT) with bright green emission. The two CPs were physically blended into single particles with ∼3 μm size, which was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and confocal fluorescence imaging. Although without any surface functionalization, the obtained CP MPs showed selective internalization into MCF-7 cancer cells over NIH-3T3 normal cells, while CP nanoparticles showed similar uptake into both cell lines. Moreover, the CP MPs could selectively kill MCF-7 cells upon NIR irradiation, which showed a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 30 μg mL−1 based on PFTTQ concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...