In situ X-ray pair distribution function analysis of accelerated carbonation of a synthetic calcium–silicate–hydrate gel†
Abstract
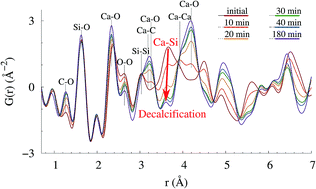
Calcium–silicate–hydrate (C–S–H) gel is the main binder component in hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) paste, and is known to play a crucial role in the carbonation of cementitious materials, especially for more sustainable alternatives containing supplementary cementitious materials. However, the exact atomic structural changes that occur during carbonation of C–S–H gel remain unknown. Here, we investigate the local atomic structural changes that occur during carbonation of a synthetic calcium–silicate–hydrate gel exposed to pure CO2 vapour, using in situ X-ray total scattering measurements and subsequent pair distribution function (PDF) analysis. By analysing both the reciprocal and real-space scattering data as the C–S–H carbonation reaction progresses, all phases present during the reaction (crystalline and non-crystalline) have been identified and quantified, with the results revealing the emergence of several polymorphs of crystalline calcium carbonate (vaterite and calcite) in addition to the decalcified C–S–H gel. Furthermore, the results point toward residual calcium being present in the amorphous decalcified gel, potentially in the form of an amorphous calcium carbonate phase. As a result of the quantification process, the reaction kinetics for the evolution of the individual phases have been obtained, revealing new information on the rate of growth/dissolution for each phase associated with C–S–H gel carbonation. Moreover, the investigation reveals that the use of real space diffraction data in the form of PDFs enables more accurate determination of the phases that develop during complex reaction processes such as C–S–H gel carbonation in comparison to the conventional reciprocal space Rietveld analysis approach.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...