Proton conducting H5BW12O40 electrolyte for solid supercapacitors
Abstract
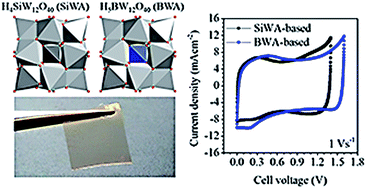
H5BW12O40 (BWA), a heteropolyacid with B3+ as the central heteroatom, was developed as an electrolyte for solid supercapacitors. The structural properties of the synthesized BWA were investigated using FTIR and XRD and were compared to those of the known silicotungstic acid (H4SiW12O40, SiWA) electrolyte. Factors affecting the cell voltage of supercapacitors using liquid BWA and SiWA electrolytes were identified using an in situ electrode potential tracking method. The respective contributions of the electrodes and electrolyte were revealed and BWA showed a wider potential window than SiWA. Solid supercapacitors enabled by BWA- and SiWA-based polymer electrolytes were demonstrated and exhibited excellent rate performance. The solid device leveraging a BWA-based polymer electrolyte achieved a cell voltage of 1.6 V, better than 1.4 V achieved by the SiWA-based device.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...