Turning periodic mesoporous organosilicas selective to CO2/CH4 separation: deposition of aluminium oxide by atomic layer deposition†
Abstract
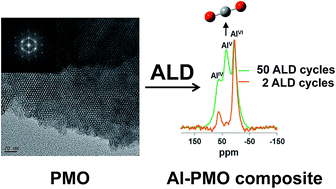
Nowadays, CO2/CH4 separation is considered extremely important with respect to making biogas economically viable. The search for efficient materials for biogas upgrading is at the cutting edge of research in the field of energy. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas (PMO) are highly suitable for application as selective adsorbents for CO2 as they have concomitant high specific surface areas and tunable surface properties. Herein, we describe the tuning of the surface properties of phenylene-PMO using atomic layer deposition (ALD) to add active aluminium species to the walls of these organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Modification with aluminium oxide was attained by varying the numbers of deposition cycles (from 2 to 100 cycles). A clear correlation between the amount of aluminium attached to PMO and the number of deposition cycles is observed. Consequently, an increase in the number of deposition cycles resulted in a reduction of the specific surface area and the pore volume of the PMO material. Variation of the number of deposition cycles to modify the surface of the PMOs yields composite materials with aluminium sites having different local coordination but the meso- and molecular-scale periodicity orders of the parent PMO remain intact. Adsorption results indicate that high selectivity for CO2/CH4 separation is obtained when pentacoordinated (AlV) and tetrahedral (AlIV) aluminium oxide are present in the PMO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...