C2N: an excellent two-dimensional monolayer membrane for He separation†
Abstract
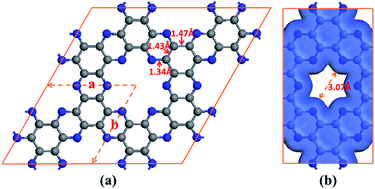
Using the first-principles density functional theory (DFT) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we investigate the He separation performance of a porous C2N monolayer synthesized recently. The DFT calculations demonstrate that the porous C2N monolayer is stable enough to be used as a gas separation membrane and the porous C2N monolayer with a suitable pore size presents a surmountable energy barrier (0.13 eV) for He molecules passing through the membrane. Furthermore, the porous C2N monolayer shows an exceptionally high selectivity for He/Ne (Ar, CH4, CO2, N2, etc.) in a wide range of temperatures. Besides, using MD simulations we demonstrate that the porous C2N monolayer exhibits a He permeance of 1 × 107 GPU at room temperature, which is much higher than the value (20 GPU) in current industrial applications. Therefore, the porous C2N monolayer should be an excellent candidate for He separation from natural gas, due to its high selectivity and excellent permeability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...