Manipulating the interfacial interactions of composite membranes via a mussel-inspired approach for enhanced separation selectivity†
Abstract
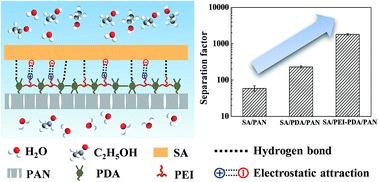
For the broadly utilized composite membranes with dense separation layers and porous support layers, the rational manipulation of interfacial interactions between these two layers is vital in optimizing the membrane structure and the associated performance. In this study, we report a facile mussel-inspired approach to enhance the separation selectivity of composite membranes by co-depositing biomimetic adhesive dopamine and poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) on a support layer and then coating with sodium alginate (SA) as the separation layer. PEI is anchored onto the support layer surface through the reaction with dopamine during the polydopamine (PDA) formation process, thus incorporating the electrostatic attraction interaction into the interface in addition to the hydrogen bond interaction between PDA and SA. Using water/alcohol separation as the model system, the separation factor of the SA/PEI–PDA/PAN membrane can reach 1807, which is 29.6 and 6.8 times higher than those of SA/PAN and SA/PDA/PAN membranes, respectively. The remarkably enhanced separation factor arises from the optimal free volume property and swelling resistance of the membrane under the optimized interfacial interactions between the separation layer and support layer. This study may present an efficient and facile approach for tailoring the membrane structure for an enhanced separation performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...