Carbon nanodots, Ru nanodots and hybrid nanodots: preparation and catalytic properties†
Abstract
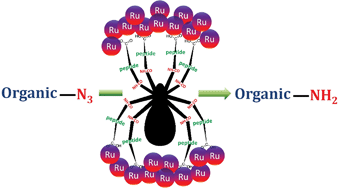
New hybrid nanodots comprised of carbon nanodots and ruthenium nanodots have been synthesized from peptide functionalized carbon nanodots and a ruthenium salt. At first, carbon nanodots have been prepared by carbonization of a synthetic tripeptide and citric acid. Then these functionalized carbon nanodots act as a template to form ruthenium nanodots from a ruthenium salt in the presence of a reducing agent, sodium borohydride in water medium. These functionalized carbon nanodots exhibit a blue emission with a high quantum yield (69.8%). Various techniques including UV-Vis, fluorescence, FTIR, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman and X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses have been used to characterize carbon nanodots and hybrid nanodots. This is a new example of preparing ruthenium nanodots by using peptide functionalized carbon nanodots as a stabilizer to form unique hybrid nanodots consisting of carbon nanodots and ruthenium nanodots in water medium. Moreover, hybrid nanodots act as a potential catalyst for the reduction of organic azides to their corresponding amines in aqueous medium. A variety of functionalized organic azides have been reduced to their corresponding amines with high yields without affecting other functionalities indicating the good chemoselectivity of the catalyst towards the azide functionality.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...