Mechanism for improving the cycle performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by RuO2 surface modification and increasing discharge cut-off potentials†
Abstract
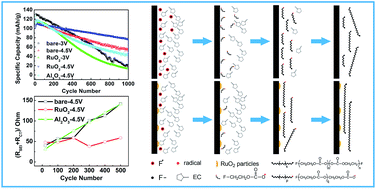
The cycle performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) is improved greatly by a surface modification with discrete RuO2 particles in combination with setting discharge cut-off potentials to 4.5 V. A specific capacity value as high as 113.8 mA h g−1 after 1000 cycles is attained. In order to not only clarify the mechanism for the improvement by the RuO2 particles deposited, but also to elucidate which chemical properties of surface-modifying materials play a critical role in the evolution of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer with cycling, the electrochemical impedance spectra and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) of a bare LNMO electrode, discrete RuO2 particle modified-LNMO electrode and discrete Al2O3 particle modified-LNMO electrode were compared. The XPS spectra of the SEI layers of these electrodes cycled between 4.5 and 5.2 V indicate that a stable SEI layer on the RuO2-modified LNMO electrode has the characteristics of higher content of LiF and longer poly-ethylenecarbonate chains with extremely low content of –CF2O– groups. The crucial point for the formation of the stable SEI layer is the sustainable consumption of the F radicals generated by the electrochemical decomposition of LiPF6 at high potentials. We conclude that the hydrolysable property of ruthenium fluorides, intermediate products obtained during the formation of the SEI layer on the RuO2-modified LNMO electrode, and the high catalytic activity of RuO2 itself for electrochemical oxygen evolution guarantee the sustainable consumption of the F radicals. Al2O3 lacks these special chemical properties to attain the sustainable consumption, thus leading to no improvement by the modification with discrete Al2O3 particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...