Effects of structural disorder and nitrogen content on the oxygen reduction activity of polyvinylpyrrolidone-derived multi-doped carbon†
Abstract
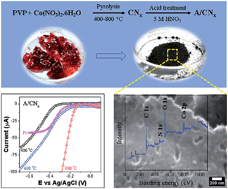
Multi-doped carbons, having high N-content (∼11 wt%, bulk) and the presence of C- and N-bound O/Co, were synthesized by pyrolysis of a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O) mixture at various temperatures (Tp) ranging from 400 to 800 °C. To study the effects of surface modification on the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity, doped carbon (CNx) samples were further acid-treated with nitric acid (HNO3). Structural characterization by Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction reveals an amorphous phase of carbon for a Tp of 400 to 700 °C, and a partially graphitic structure for a Tp of 800 °C. The electrocatalytic performance of the as-synthesized and acid-treated CNx determined by linear sweep as well as cyclic voltammetry in 0.1 mol L−1 KOH electrolyte reveals significant catalytic activities with an ORR onset potential of −144 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl), as compared to −210 mV for a Pt electrode under similar conditions. Correlations between the electrochemical parameters and structural parameters such as the degree of disorder and N-content suggest high electrocatalytic activity for CNx with low disorder and high N-content. In addition to their high ORR activity, the CNx samples synthesized at lower Tp also exhibit catalytic activity for methanol oxidation, which makes them suitable catalyst supports for direct methanol fuel cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...