Impact of large-scale meso- and macropore structures in adenosine-derived affordable noble carbon on efficient reversible oxygen electrocatalytic redox reactions†
Abstract
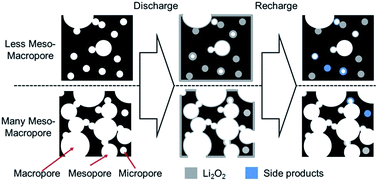
In this report, we delineate a successful synthesis of a high performance and affordable adenosine-derived noble carbon cathode for LOBs with bifunctional electrocatalytic activity and show that the pore structure of the cathode is a key feature to control the electrochemical performance of this electrochemical system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...