Electrochemical performance of α-MoO3–In2O3 core–shell nanorods as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
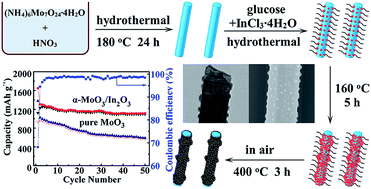
α-MoO3–In2O3 core–shell nanorods were prepared by a facile two-step hydrothermal method. As the anode of lithium-ion batteries, their reversible capacity was up to 1304 mA h g−1 at 0.2 C rate (5 hours per half cycle) and maintains 1114 mA h g−1 after 50 cycles. At a rate of 0.3 C, 0.5 C, 1 C and 2 C, the discharge capacities after 50 cycles were maintained at 938, 791, 599 and 443 mA h g−1, respectively. The enhanced electrochemical performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effect between α-MoO3 and In2O3, one-dimensional core–shell nanostructures, short paths for lithium diffusion and interface spaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...