Wet-chemical nitrogen-doping of graphene nanoplatelets as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
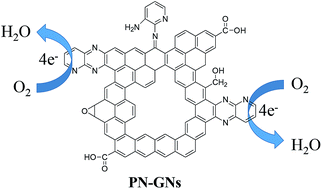
We report a facile wet-chemical approach for the preparation of high-quality pyridinic N-rich nitrogen-doped graphene nanoplatelets (PN-GNs). Efficient doping of nitrogen atoms into two-dimensional graphene networks can be achieved via an acid-catalyzed dehydration reaction between GO and primary amine-containing small molecules. The nitrogen content in PN-GNs can easily be controlled over a wide range (3.27–15.28 wt%) by simple variation of the molar feed ratio of reactants. Furthermore, specific pyridinic nitrogen configurations, considered beneficial for the ORR process, can be incorporated into the PN-GNs. This results in the efficient structural restoration of graphene structures during the reaction. Therefore, these unique features of PN-GNs allow them to show superior electrocatalytic activities (high selectivity, excellent long-term stability and good tolerance to methanol crossover) toward the ORR in an alkaline electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...