Engineered graphene–nanoparticle aerogel composites for efficient removal of phosphate from water
Abstract
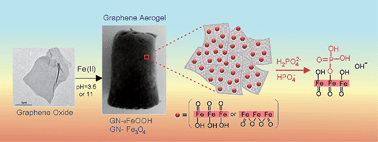
The contamination of aqueous systems with phosphates has considerable environmental concerns and here, we present a new method for phosphate removal based on graphene aerogel composites. 3-Dimensional graphene aerogels decorated with goethite (αFeOOH) and magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles were synthesised and their application in capturing phosphates in water was successfully demonstrated. The prepared aerogels showed superior capacity to remove up to 350 mg g−1 at an initial phosphate concentration of 200 mg L−1 from water. The Freundlich model was suitable to describe the adsorption mechanism of phosphate removal by the graphene–iron nanoparticle aerogels through both mononuclear and polynuclear adsorption onto the nanosized αFeOOH and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. These new phosphate adsorbents can be produced in different forms and dimensions, using a simple, green and scalable process, and have the potential to be applied for practical applications in phosphate management of waste and storm water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...