Surfactants assisted synthesis of nano-LiFePO4/C composite as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
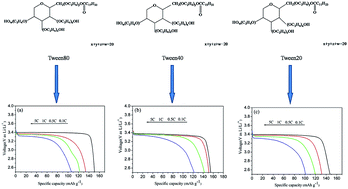
The goal of this research was to study the effect of molecular structure surfactant on the performance of LiFePO4/C composite. The solid state reaction method was applied to prepare a series of LiFePO4/C materials by adding various surfactants. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Infrared spectrum analysis (FTIR), Raman spectral analysis and electrochemical methods. The results confirm the existence of interactions between the surfactant molecules and the precursor that contribute to the formation of nanoparticles and a homogeneous carbon coating layer on the surface. The structure of the surfactants played an important role in improving the performance of LiFePO4/C composites. The structures of surfactants affect the particle size and the amount of graphite-like carbons of LiFePO4/C composites. The surfactant with longer alkyl C–C chain length could effectively prevent particle growth, while the surfactant with shorter alkyl C–C chain length form more graphene-like carbon during pyrolysis. The as-prepared LiFePO4/C particles using various surfactants show different electrochemical performances. According to Raman spectroscopy and EIS analysis, these composites have different ID/IG peak ratios and charge transfer resistance. Especially, LiFePO4/C synthesis with composite surfactant (weight ratio of Tween80 to Tween20 equal to 1.5) showed an excellent electrochemical performance with a discharge capacity of 167.3 mA h g−1 at 0.1 C rate and 129.4 mA h g−1 at 5 C rate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...