Structural stability of BTTB-based metal–organic frameworks under humid conditions†
Abstract
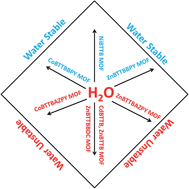
Stability of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) under humid environments is of particular interest for their potential commercial and industrial uses. In this work, water vapor adsorption experiments and subsequent structural analysis on the newly synthesized BTTB-based MOFs (BTTB = 4,4′,4′′,4′′′-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetrayltetrabenzoic acid) have been performed to investigate their stability under humid conditions. ZnBTTB and CdBTTB degrade completely after exposure to 90% relative humidity (RH). The instability of ZnBTTB is due to the four-coordinated zinc carboxylate system similar to MOF-5. Similarly, CdBTTB is also unstable as Cd2+ ions have coordination number of 4 when the MOF is activated (desolvated). Unlike ZnBTTB and CdBTTB, the structure of ZnBTTBBDC has not degraded significantly upon exposure to 90% RH. This partial structure retention is attributed to the higher nuclearity of metal in the SBU of ZnBTTBBDC and higher metal coordination number compared to ZnBTTB and CdBTTB. Water adsorption isotherms of CoBTTBAZPY and ZnBTTBAZPY show type V behavior due to free nitrogen sites. The crystal structures of AZPY-based pillared MOFs show partial loss of crystallinity whereas BPY-based pillared MOFs remain stable after exposure to 90% RH. The greater stability of BPY-based MOFs is attributed to the higher extent of catenation, higher rigidity of the BPY linker, and absence of any hydrophilic sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...