Effects of hydrodynamic interactions on the crystallization of passive and active colloidal systems
Abstract
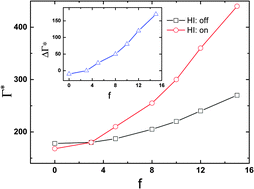
Effects of hydrodynamic interactions (HI) on the crystallization of a two-dimensional suspension of colloidal particles have been investigated, by applying a multiscale simulation method combining multiparticle collision dynamics for solvent particles with standard molecular dynamics for the colloids. For a passive system, we find that HI slightly shifts the freezing point to a smaller density, while the equilibrium structure remains nearly unchanged for a given global order parameter. For an active system, however, HI can significantly shift the freezing density to a higher value and the freezing transition becomes more continuous compared to its passive counterpart. This HI-induced shift becomes more remarkable with increasing propelling force. In addition, HI may also enhance the structural heterogeneities in an active system. For both passive and active systems, it is shown that HI can accelerate the relaxation process to their final steady state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...