The effect of surface charge on the boundary slip of various oleophilic/phobic surfaces immersed in liquids
Abstract
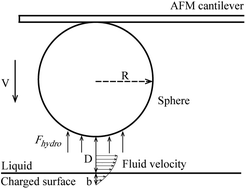
The reduction of fluid drag is an important issue in many fluid flow applications at the micro/nanoscale. Boundary slip is believed to affect fluid drag. Slip length has been measured on various surfaces with different degrees of hydrophobicity and oleophobicity immersed in various liquids of scientific interest. Surface charge has been found to affect slip length in water and electrolytes. However, there are no studies on the effect of surface charge on slip at solid–oil interfaces. This study focuses on the effect of surface charge on the boundary slip of superoleophilic, oleophilic, oleophobic, and superoleophobic surfaces immersed in deionized (DI) water and hexadecane and ethylene glycol, based on atomic force microscopy (AFM). The surface charge was changed by applying a positive electric field to the solid–liquid interface, and by using liquids with different pH values. The results show that slip length increases with an increase in applied positive electric field voltage. Slip length also increases with a decrease in the pH of the solutions. The change in slip length is dependent on the absolute value of the surface charge, and a larger surface charge density results in a smaller slip length. In addition, the surface charge density at different solid–liquid interfaces is related to the dielectric properties of the surface. The underlying mechanisms are analyzed.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...