Effects of interaction between a polycation and a nonionic polymer on their cross-assembly into mixed micelles†
Abstract
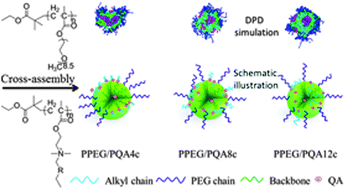
In this paper, to investigate the effects of interactions between poly(quaternary ammonium) salts (PQAs) and poly(ethylene glycol) on their mixed micellar surface structures and properties under spontaneous conditions, a series of PQAs were first designed and synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) using 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) quaternized by bromobutane, bromooctane, and bromododecane, respectively. Poly(poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate) (PPEG) with a similar degree of polymerization was also prepared using poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate by ATRP. Next, these PQAs were mixed with an equal weight of PPEG in water to cross-assemble into mixed micelles. The structures and features of these mixed micelles were characterized by fluorescence measurements, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), phase analysis light scattering (PALS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), and hydrogen–hydrogen correlation spectroscopy nuclear magnetic resonance (H–H COSY NMR). These results suggest that PQAs and PPEG mixtures can cross-assemble into mixed micelles with low CMC. The surface structures, particle sizes, size distributions, and zeta potentials of PQAs and PPEG mixtures can be tailored by varying the alkyl chain length in quaternary ammonium salts, and the alkyl chain length also influences the distribution and the alkyl chain orientation of quaternary ammonium salts on mixed micelle surfaces. In addition, cytotoxicity of these mixed micelles can be markedly reduced by PPEG compared with their corresponding PQAs, but their good antibacterial activities are still maintained to a certain degree, as evaluated by methyl tetrazolium assay (MTT) and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Our present work provides a new avenue for the preparation of biocompatible and antibacterial materials for biomedical applications.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...