C–H bond activation induced by thorium metallacyclopropene complexes: a combined experimental and computational study†
Abstract
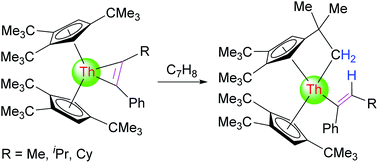
Inter- and intramolecular C–H bond activations by thorium metallacyclopropene complexes were comprehensively studied. The reduction of [η5-1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2]2ThCl2 (1) with potassium graphite (KC8) in the presence of internal alkynes (PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CR) yields the corresponding thorium metallacyclopropenes [η5-1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2]2Th(η2-C2Ph(R)) (R = Ph (2), Me (3), iPr (4), C6H11 (5)). Complexes 3–5 derived from phenyl(alkyl)acetylenes are very reactive resulting in an intramolecular C–H bond activation of the 1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2 ligand. In contrast, no intramolecular C–H bond activation is observed for the diphenylacetylene derived complex 2, but it does activate α-C–H bonds in pyridine or carbonyl derivatives upon coordination. Density functional theory (DFT) studies complement the experimental studies and provide additional insights into the observed reactivity.
CR) yields the corresponding thorium metallacyclopropenes [η5-1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2]2Th(η2-C2Ph(R)) (R = Ph (2), Me (3), iPr (4), C6H11 (5)). Complexes 3–5 derived from phenyl(alkyl)acetylenes are very reactive resulting in an intramolecular C–H bond activation of the 1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2 ligand. In contrast, no intramolecular C–H bond activation is observed for the diphenylacetylene derived complex 2, but it does activate α-C–H bonds in pyridine or carbonyl derivatives upon coordination. Density functional theory (DFT) studies complement the experimental studies and provide additional insights into the observed reactivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...