Alkyl-nitrile adlayers as probes of plasmonically induced electric fields†
Abstract
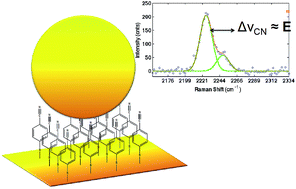
Vibrational Stark shifts observed from mercaptoalkyl monolayers on surface enhanced Raman (SERS) active materials are reported to provide a direct measurement of the local electric field around plasmonic nanostructures. Adlayers of CN−, p-mercaptobenzonitrile, and n-mercaptobutylnitrile were adsorbed to a heterogeneous nanostructured Ag surface. The frequency of the CN moiety was observed to shift in a correlated fashion with the SERS intensity. These shifts are attributed to a vibrational Stark shift arising from rectification of the optical field, which gives rise to a DC potential on the surface. All three molecules showed CN Stark shifts on the plasmonic surfaces. p-Mercaptobenzonitrile is observed to be a well-behaved probe of the electric field, providing a narrow spectral line, suggesting a more uniform orientation on the surface. The utility of p-mercaptobenzonitrile was demonstrated by successfully assessing the electric field between gold nanoparticles adsorbed to a monolayer of the nitrile on a flat gold surface. A model is presented where the Stark shift of the alkyl-nitrile probe can be correlated to optical field, providing an intensity independent measurement of the local electric field environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...