Investigating linear and nonlinear viscoelastic behaviour and microstructures of gelatin-multiwalled carbon nanotube composites†
Abstract
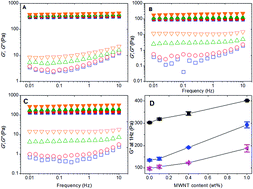
We have investigated the linear and nonlinear rheology of various gelatin-multiwalled carbon nanotube (gel-MWNT) composites, namely physically-crosslinked-gelatin gel-MWNT composites, chemically-crosslinked-gelatin gel-MWNT composites, and chemically–physically-crosslinked-gelatin gel-MWNT composites. Further, the internal structures of these gel-MWNT composites were characterized by ultra-small angle neutron scattering and scanning electron microscopy. The adsorption of gelatin onto the surface of MWNT is also investigated to understand gelatin-assisted dispersion of MWNT during ultrasonication. For all gelatin gels, addition of MWNT increases their complex modulus. The dependence of the storage modulus with frequency for gelatin-MWNT composites is similar to that of the corresponding neat gelatin matrix. However, by incorporating MWNT, the dependence of the loss modulus on frequency is reduced. The linear viscoelastic region is decreased approximately linearly with the increase of MWNT concentration. The pre-stress results demonstrate that the addition of MWNT does not change the strain-hardening behaviour of physically-crosslinked gelatin gel. However, the addition of MWNT can increase the strain-hardening behaviour of chemically-crosslinked gelatin gel, and chemically–physically crosslinked gelatin gel. Results from light microscopy, cryo-SEM, and USANS demonstrate the hierarchical structures of MWNT, including that tens-of-micron scale MWNT agglomerates are present. Furthermore, the adsorption curve of gelatin onto the surface of MWNT follows a two-stage pseudo-saturation behaviour.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...