Synthesis and evaluation of 6-substituted 3-arylcoumarin derivatives as multifunctional acetylcholinesterase/monoamine oxidase B dual inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease†
Abstract
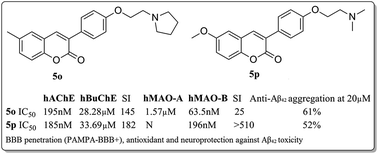
Considering the complex etiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), multifunctional agents may exhibit important properties against this disease. A series of 6-substituted 3-arylcoumarins (5a–t) were designed, synthesized and evaluated as cholinesterase (ChE) and monoamino oxidase (MAO) inhibitors. Among them, compounds 5o [IC50, 195 nM for human acetylcholinesterase (hAChE), selectivity index, SI (human butyrylcholinesterase, hBuChE/hAChE) = 145; IC50, 63.5 nM for human monoamine oxidase-B (hMAO-B), SI (human monoamine oxidase-A, hMAO-A/hMAO-B) = 25] and 5p [IC50, 185 nM for hAChE, SI (hBuChE/hAChE) = 182; IC50, 196 nM for hMAO-B, SI (hMAO-A/hMAO-B) > 510] were found to selectively inhibit both hAChE and hMAO-B with IC50 values in the nanomolar range. The abilities of 5o and 5p to bind to hAChE and hMAO-B were confirmed by molecular docking and kinetic studies. Moreover, 5o and 5p were found to exhibit significant inhibition of self-induced Aβ42 aggregation (61% and 52%, at 20 μM), have antioxidant properties (0.81 and 1.17 trolox equivalent by ABTS assay), provide neuroprotection against Aβ42-induced cytotoxicity and blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration capacity (PAMPA-BBB+), and are thus potential anti-Alzheimer agents with balanced activities. Overall, the study provided meaningful information for further development of multifunctional drugs for AD therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Towards understanding and treating Alzheimer’s disease

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...