An algal process treatment combined with the Fenton reaction for high concentrations of amoxicillin and cefradine
Abstract
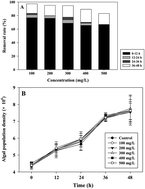
The goal of the current study was to create a combined technique for the removal of two common antibiotics (amoxicillin and cefradine) using Fenton and an algal action process. The removal capacity of the individual algal treatment and the combined system was evaluated. The green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa had compound-dependent removal efficiency. Due to the high tolerance of the algae to the impact of the antibiotics, most of the target compound amoxicillin (approximately 90%) were treated after a 48 h algal treatment at a relevant lower concentration (100, 200 and 300 mg L−1). However, when the concentration of the treated antibiotic increased to 400 and 500 mg L−1, the final removal rate decreased to less than 90%. For cefradine, the removal efficiency was always unsatisfactory at any of the given five concentrations. Additionally, compared with the removal capacity of the individual algal treatment, a higher removal rate and a shorter treatment time were achieved using the combined Fenton-algal treatment, even when the relevant concentrations were increased to 1 g L−1 for the two target concentrations. Our results also indicated that a reduced amount of the Fenton reagent could not decrease the efficiency of the Fenton treatment process, and the removal contribution using the subsequent algal action was improved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...