Development of a julolidine-based interfacial modifier for efficient inverted polymer solar cells†
Abstract
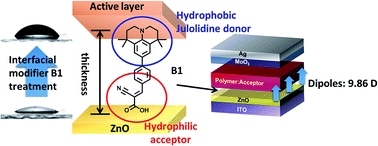
To enhance the performance of inverted polymer solar cells (PSCs), we have designed and synthesized interfacial modifiers (IMs) which provide better surface properties for the ZnO layer. The synthesized IMs were composed of electron donating and accepting parts. Julolidine or diethyl aniline was used as a donor part, and cyano acrylic acid as an acceptor part. The julolidine-based B1 material exhibited a much stronger dipole moment of 9.86 D than diethyl aniline-based B2 (9.17 D), and the water contact angle of the ZnO surface treated with B1 (65.3°) was much larger than that with B2 (39.8°). These julolidine effects were much more powerful than diethyl aniline: the julolidine moiety significantly decreased the hydrophilicity of the ZnO surface and its work function (WF). The inverted devices with the configuration of ITO/ZnO/IMs (B1 or B2)/PTB7-Th:PC71BM/MoO3/Ag were fabricated and the photovoltaic properties were investigated. Both B1 and B2 worked well as IMs, but B1-treated devices exhibited a much higher power conversion efficiency of 8.35% than B2-treated devices (7.80%). B1 treatment on ZnO effectively reduced series resistance and leakage current in the devices due to the julolidine effects. We believe that julolidine is an excellent electron donating building block for IMs in inverted PSCs and our approach can be applied to other IM systems universally to improve photovoltaic performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...