Additive-free 1,4-butanediol mediated synthesis: a suitable route to obtain nanostructured, mesoporous spherical zinc oxide materials with multifunctional properties†
Abstract
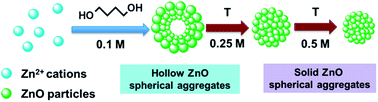
A family of mesoporous, self-aggregated zinc oxide materials with spherical morphologies of high crystalline quality, is obtained through a facile, additive-free polyol procedure. The forced hydrolysis of zinc acetylacetonate in 1,4-butanediol (BD), in various reaction conditions, affords ZnO materials with versatile morphologies and optical properties. The reaction parameters (temperature, time and zinc source concentration) modulate the ZnO nanocrystallites size (from 8.1 to 13.2 nm), the spheres diameter (ranging from 50 up to 250 nm), the internal structure of the spherical aggregates (hollow or solid) and their specific surface area (from 31 to 92 m2 g−1). Polycrystalline spheres with hollow cores are obtained at the lowest temperature (90 °C) and zinc cation concentration (0.1 M), while at higher reaction temperatures (140–180 °C), solid spherical aggregates are developed. A reaction mechanism for ZnO formation via zinc layered hydroxide (LDH-Zn) is proposed based on nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR and 13C NMR) and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. The obtained ZnO materials have a functionalized surface, derived from the polyol and act as a nitrogen selective photocatalyst in the reduction reaction of NO3−. The organic residual attached on the ZnO surface plays a crucial role in the denitrification reaction, since the photo-cleaned sample showed negligible photocatalytic activity. The ZnO materials also exhibited microbicidal and anti-biofilm activity against reference and clinical strains, highlighting their potential for the development of novel antimicrobial formulations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...