A well-defined polyelectrolyte and its copolymers by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization: synthesis and applications†
Abstract
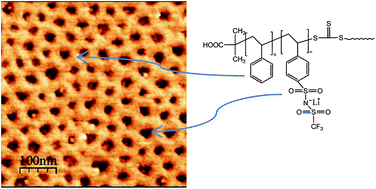
Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) polymerization of 4-styrenesulfonyl(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide potassium salt (SKTFSI) in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solution was carried out using 2-(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonylsulfanyl)-2-methylpropionic acid (DDMAT) as a reversible chain transfer agent in the presence of 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) at 65 °C in an inert atmosphere. We showed both homopolymers and well-defined polyelectrolyte diblock copolymer systems could be prepared through the direct polymerization of the charged SKTFSI monomer. To produce Li-ion polyelectrolytes, a cation exchange methodology (e.g. K+ → Li+) was used. Self-assembly of single-ion diblock copolymer thin films consisting of a Li-ion conductive PSLiTFSI block associated with a glassy polystyrene block is also demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...