One step preparation of quantum dot-embedded lipid nanovesicles by a microfluidic device†
Abstract
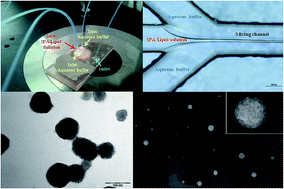
Synthetic carriers that mimic “natural lipid-based vesicles” (such as micro/nanovesicles, exosomes) have found broad applications in biomedicine for the delivery of biomolecules and drugs. Remarkable advantages of using synthetic carriers include control over the lipid composition, structure and size, together with the possibility to add tracer molecules to monitor their in situ distribution via fluorescence microscopy. Over the past few years, new methods of vesicles production have been developed and optimized, such as those based on microfluidic techniques. These innovative approaches allow us to overcome the limitations faced in conventional methods of liposome preparation, such as size distribution and polydispersity. Herein, a Microfluidic Hydrodynamic Focusing (MHF) device has been used for the production of lipid-based vesicles with different lipid combinations that resemble natural exosomes, such as phosphatidylcholines (PC), cholesterol (Chol), dicetyl phosphate (DCP) and ceramide (Cer). Thanks to a fine control on fluid manipulation, the MHF device allows preparation of vesicles with controlled size, a relevant feature in the emerging field of carrier-assisted cell-delivery. Interestingly, PC/Chol/Cer vesicles exhibit low polydispersity and high stability up to 45 days. Later, quantum dots (QDs) were successfully embedded in these vesicles through the same preparation process. The development of QD-embedded lipid nanovesicles by MHF devices has never been described previously.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...