CuInSe2 thin film solar cells prepared by low-cost electrodeposition techniques from a non-aqueous bath
Abstract
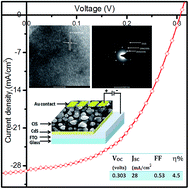
Polycrystalline CuInSe2 (CIS) thin films have been prepared by low-cost electrochemical method from non-aqueous ethylene glycol solvent onto cadmium sulfide (CdS) thin films. The co-deposition potential for Cu, In and Se was optimized with cyclic voltammetry measurements. CIS layers were electrodeposited at −1.1, −1.3 and −1.5 V versus Ag/AgCl references in an air-tight custom made electrodeposition cell. The films were selenized at 400 °C for 20 minutes. The optical, structural, morphological, compositional and optoelectronic properties of as-prepared and selenized samples were studied using UV-Vis spectrophotometery, X-ray diffractometery, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX) and current–voltage (I–V) measurements. Three prominent sharp peaks of tetragonal CIS, (112), (204)/(220), and (312/116) were revealed in all as-prepared and selenized samples. Upon selenization the crystallinity of the samples was found to be improved remarkably. Compact, void free, and nearly uniform thin films of grain size ∼1 μm were deposited. The as-deposited and selenized CIS samples were Cu-rich whereas the content of Se was ∼50% obtained by EDAX analysis. The value of inter-planer distance, d = 3.339 Å, measured by HRTEM corresponds to the (112) plane of a tetragonal CIS crystal structure. The circular spotted rings observed in the selected area diffraction (SAD) pattern were confirmed as (112), (204)/(220) and (312)/(116) reflections of CIS. The solar cell parameters, Voc, Jsc, FF and efficiency (η) were found to be 303 mV, 28 mA cm−2, FF ∼ 53% and η = 4.5% for the CIS film deposited at −1.5 V. The values of shunt conductance, GD = 2.5 mS cm−2 and GL = 7.9 mS cm−2 and series resistance, RD = 0.81 Ω cm2 and RL = 0.19 Ω cm2 were calculated for dark and illuminated conditions. Mott–Schottky analysis was also carried out on the final solar cell in dark and illuminated conditions to study the carrier concentration and defects in the CdS/CIS interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...