Chitosan-graft-PAMAM–alginate core–shell nanoparticles: a safe and promising oral insulin carrier in an animal model†
Abstract
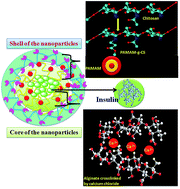
The development of efficient, biodegradable and bio-safe polymeric nanocarriers for oral insulin delivery is a major goal in the biomedical field. PAMAM grafted chitosan (CS-g-PAMAM) was prepared using a Michael type addition reaction to graft polyamidoamine (PAMAM) onto native chitosan to improve the water solubility, pH responsiveness, and insulin encapsulation efficiency for the enhancement of the relative oral bioavailability of insulin. The insulin loaded nanoparticles were prepared by the formation of an ionotropic pre-gel with an alginate (ALG) core that entrapped insulin, followed by PAMAM grafted chitosan (CS-g-PAMAM) polyelectrolyte complexation. The mild preparation process not involving harsh chemicals is aimed to improve insulin bio-efficiency in vivo. The nanoparticles had an excellent core–shell architecture with an average particle size of 98–150 nm as shown by dynamic light scattering (DLS), with ∼97% insulin encapsulation and 27% insulin loading capacity. In vitro release data confirm a pH sensitive and self-sustained release of encapsulated insulin, protecting it from enzymatic deactivation in the gastrointestinal tract. The oral administration of these nanoparticles exhibits a pronounced hypoglycaemic effect in diabetic mice, producing a relative bioavailability of ∼11.78%. As no acute systemic toxicity is observed with peroral treatment, these core–shell nanoparticles can effectively serve as an efficient carrier of oral insulin in a mouse model.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...