Two novel and simple strategies for improvement of the traditional activation method for activated carbon preparation: nano-copper catalysis and Cu(ii) doping
Abstract
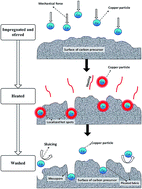
The present study explores the possibilities of employing copper nanoparticles (nano-copper) as catalyst and copper(II) chloride as doping agent in the activation process to prepare activated carbons from Platanus orientalis leaves by H3PO4 activation. The three types of carbons by original H3PO4 activation, nano-copper catalytic activation and Cu(II) doping activation were identified as AC, AC-Cu, and AC-Cu(II), respectively. These carbons were characterized by thermogravimetric analyses (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), BET surface area analysis and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The effects of nano-copper and copper(II) chloride on the activation of these carbons were compared and discussed. The methylene blue adsorption capacities were also studied. Thermal analysis results illustrated that introduction of nano-copper and copper(II) chloride into the activation process accelerated the decomposition of the precursor. The surface areas of AC, AC-Cu and AC-Cu(II) were 1043.967, 822.627 and 1118.900 m2 g−1, respectively. All the three types of carbon exhibited relatively high pore volume compared to those activated carbons with similar surface areas. AC-Cu possessed more surface functional groups than the other two samples. The three types of carbon presented high methylene blue adsorption capacities; in particular, AC-Cu and AC-Cu(II) adsorbed more methylene blue than AC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...