A multifunctional hierarchically assembled magnetic nanostructure towards cancer nano-theranostics
Abstract
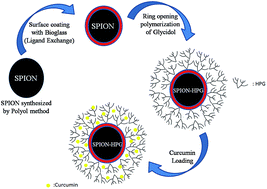
Nowadays, iron oxide nanoparticles are among the most interesting carriers in simultaneous drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging applications (theranostics). In this study, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized by a co-precipitation method followed by coating with an active-bioglass layer. This nanostructure is functionalized with hyperbranched polyglycerol through ring-opening polymerization of glycidol. The carrier was characterized using TEM, FT-IR, XRD, TGA, and elemental analysis. The results showed that the diameter of the carrier was between 20–30 nm. The cytotoxicity and cellular uptake results indicated that this nanostructure did not induce any cytotoxicity while expressing good potential as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Moreover, curcumin was loaded on the carrier as a hydrophobic sample drug. The results showed a significant increase in curcumin solubility, which revealed the potential of this nanostructure in simultaneous cancer diagnosis and therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...