Arginyl-glutamine dipeptide attenuates experimental colitis by enhancing antioxidant function and inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB†
Abstract
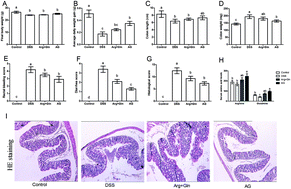
This study aimed to investigate the effect and underlying mechanism of Arginyl-glutamine (AG) dipeptide on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis by in vivo and in vitro models. Acute colitis was induced in ICR mice by administering 5% DSS. 1% AG and 0.5% glutamine and 0.5% arginine were fed via mixing in the basic diet after colitis induction. The results showed that AG could reverse the diverse effects on average daily weight gain, colon weight, rectal bleeding score, diarrhea score, and histological score caused by DSS. Meanwhile, dietary AG supplementation attenuated DSS-induced oxidative stress and improved the antioxidant system in mice. Although AG failed to improve intestinal dysfunction, inflammatory response was markedly reduced in DSS-induced colitis after AG treatment. Ultimately, AG inhibited IKK phosphorylation and subsequent nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) activity and its translocation into the nucleus. From the in vitro study, AG was found to improve cell viability, antioxidant function, and monolayer permeability and reduce inflammatory response in DSS-challenged Caco-2 cells. In conclusion, AG protected mice against DSS-induced colitis via increasing the antioxidant system and down-regulating proinflammatory cytokines. The inhibition of NF-κB activation might be part of the mechanism underlying the effects of AG on the colitis model.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...