A soft-template mediated approach for Au(0) formation on a heterosilica surface and synergism in the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol†
Abstract
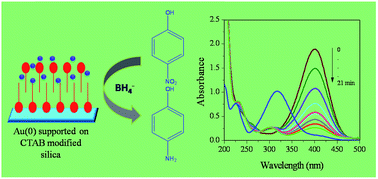
Under suitably controlled conditions a cationic surfactant e.g. cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) forms bilayers on a silica surface, which has the unique property of solubilizing organic molecules through ‘adsolubilization’. This property is judiciously exploited to adsorb AuCl4− ions on the modified silica surface at much higher loading (compared to normal silica) through the formation of a CTA+ AuCl4− complex on the silica support. Next, gold nanoparticles supported on the surfactant-modified silica (SMS) are prepared using two methods: (1) UV illumination and (2) borohydride reduction, and the materials are designated as SMSG-1 and SMSG-2. Characterization of the particles confirms the formation of Au(0) nanoparticles on the SMS surface. The particles have a spherical shape with an average size of 37 ± 11 and 54 ± 14 nm for SMSG-1 and SMSG-2, respectively. They exhibit much higher catalytic activity when compared to Au(0) supported on normal silica for 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) reduction in a borohydride medium. Such synergism is presumed to be due to the surfactant bilayer, which provides a high concentration of 4-nitrophenolate ions near the Au(0) nanoparticles embedded on the SMS leading to highly efficient contact between them. The reductions under different conditions are studied and compared. SMSG-1 shows better performance when compared to SMSG-2. While the reaction followed a pseudo-first order for SMSG-1 for all experimentally studied conditions, a clear change over in order from first to second was noticed for SMSG-2 under certain conditions. The reaction rates, recyclability and turn over frequency (TOF) with a growing micro-electrode (GME) and a fully grown micro-electrode (FGME) are compared. The GME shows ∼9 times higher catalytic activity as compared to the FGME.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...