Metabolomics approach to identify therapeutically potential biomarkers of the Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang decoction effect on the hepatoprotective mechanism†
Abstract
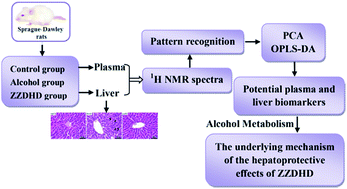
Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang decoction (ZZDHD), a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formula, has been widely used for the treatment of alcohol-induced liver injury for many years. To comprehensively explore the possible mechanism of the hepatoprotective effects of ZZDHD, a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolomics study, 1H NMR spectra combined with pattern recognition methods including PCA and OPLS-DA, was applied to identify potential plasma and liver biomarkers responsible for the positive effects of ZZDHD on alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. PCA gave a global overview of control, alcohol and ZZDHD group rats. Potential plasma and liver biomarkers that were obtained from OPLS-DA loading plots combined with the corresponding VIP values reflected the hepatoprotective effects of ZZDHD associated with alcohol-induced liver injury. The results suggested that 9 potential plasma biomarkers including, lipoprotein, leucine, valine, dihydrothymine, 3-D-hydroxybutyrate, lactate, alanine, acetate and glucose, and 8 potential liver biomarkers, triglyceride, lactate, alanine, acetate, glutamine, glucose, xanthine and hypoxanthine were identified. Related metabolic pathway analysis found that ZZDHD significantly alleviated the disturbance in energy metabolism, glucose metabolism, amino acid metabolism, lipid metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, ameliorating lipid peroxidation and permeability change of membrane, and oxidative stress induced by alcohol. The results indicated that ZZDHD could achieve remarkable effects on alcoholic hepatic injury through partially preventing or regulating the perturbed metabolic pathways. The study also demonstrated that NMR-based metabolomics was a useful tool for screening potential biomarkers, further helping to explain the therapeutic mechanism of TCM formula on a comprehensive scale.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...