An ultrasensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide/carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotube/ionic liquid/gold nanoparticle composites for vanillin analysis
Abstract
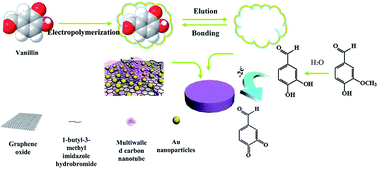
An imprinted electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide/carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotube/ionic liquid/gold nanoparticles/molecularly imprinted polymers (GO/CCNTs/IL/AuNPs/MIPs) has proved highly ultrasensitive and selective in the analysis of vanillin in spiked water samples. The GO/CCNTs/IL/AuNPs composite was utilized to improve the electrochemical response and sensitivity of the sensor. The molecularly imprinted polymer membrane was prepared by electropolymerization and could specifically determine vanillin. Under optimized conditions, the prepared molecular imprinting electrode material showed fast rebinding dynamics, and was successfully applied to vanillin detection with a wide linearity range from 1.00 × 10−8 to 2.50 × 10−6 mol L−1 and a detection limit of 6.23 × 10−10 mol L−1. The proposed imprinted electrochemical sensor also exhibited high repeatability (relative standard deviation of 3.16%) and stability (3.8%) for the analysis of real samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...