Conducting poly(o-anisidine-co-o-phenyldiammine) nanorod dispersed epoxy composite coatings: synthesis, characterization and corrosion protective performance†
Abstract
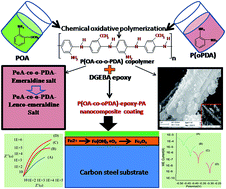
Conducting polymers (CPs) have been significantly contributing to the development of high performance new-generation anti-corrosive coatings. CP nanofiller dispersed insulating polymer coatings effectively prevent the transport of corrosive ions (H+, O2−, Cl−, OH− etc.) at the coating–metal interface, via a barrier or redox mechanism. In view of this, for the first time, we report the synthesis of poly(o-anisidine-co-o-phenyldiammine) P(oA-co-oPDA) copolymer conducting nanorods. Poly(o-anisidine) (PoA) conducting nanoparticles were also synthesized laterally. The formulations of these nanofiller dispersed epoxy-polyamide (PA) nanocomposite coating systems have also been reported. The structural elucidation was performed by FT-IR, UV-Vis, and 1H NMR spectroscopy. The crystallinity, surface area and morphology of the fillers were analysed by XRD, BET, SEM and TEM techniques. The thermal stability and hydrophobic behaviour were investigated using TGA, DSC and contact angle measurements. The physico-mechanical properties and corrosion protective performance of these coatings were evaluated using standard methods. The salt spray test, potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) and electron impedance spectroscopy studies (EIS) were conducted in 5 wt% NaCl and 5 wt% HCl media. The physico-mechanical properties, corrosion protection performance and Raman studies revealed that the P(oA-co-oPDA)-epoxy-PA nanocomposite coating exhibited superior performance when compared to PoA-epoxy-PA, epoxy-PA and other such nanocomposite coatings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...