Advanced treatment of acrylic fiber manufacturing wastewater with a combined microbubble-ozonation/ultraviolet irradiation process
Abstract
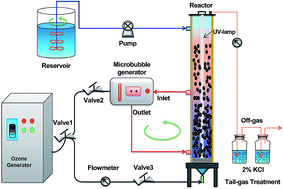
This work investigated the effectiveness of a combination of microbubble-ozonation and ultraviolet (UV) irradiation for the treatment of secondary wastewater effluent of a wet-spun acrylic fiber manufacturing plant. Under reactor condition (ozone dosage of 48 mg L−1, UV fluence rate of 90 mW cm−2, initial pH of 8.0, and reaction time of 120 min), the biodegradability (represented as BOD5/CODcr) of the wastewater improved from 0.18 to 0.47. This improvement in biodegradability is related to the degradation of alkanes, aromatic compounds, and other bio-refractory organic compounds. The combination of microbubble-ozonation and UV irradiation synergistically improved treatment efficiencies by 228%, 29%, and 142% for CODcr, UV254 removal and BOD5/CODcr respectively after 120 min reaction time, as compared with the sum efficiency of microbubble-ozonation alone and UV irradiation alone. Hydroxyl radical production in the microbubble-ozonation/UV process was about 1.8 times higher than the sum production in microbubble-ozonation alone and UV irradiation alone. The ozone decomposition rate in the combined process was about 4.1 times higher than that in microbubble-ozonation alone. The microbubble-ozonation/UV process could be a promising technique for the treatment of bio-refractory organics in the acrylic fiber manufacturing industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...