Selective electrochemical detection of dopamine using nitrogen-doped graphene/manganese monoxide composites
Abstract
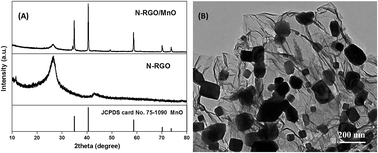
Nitrogen doping plays a critical role in regulating the electronic properties of graphene, which has shown fascinating applications in bioelectronics and biosensors. Besides, the surface properties of graphene could be adjusted via chemical modification, which facilitates its use in composite materials. Furthermore, a covalent assembly of graphene into an ordered hierarchical structure provides an interconnected conductive network beneficial to electrolyte transfer on the electrode surface. In this paper, we developed a novel nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide/manganese monoxide composite (N-RGO/MnO) by incorporating a covalent assembly and nitrogen doping. The as prepared N-RGO/MnO was further applied for highly selective and sensitive detection of dopamine (DA) in the presence of uric acid (UA) and ascorbic acid (AA) by differential pulse voltammetry. The separation of the oxidation peak potentials for DA-UA was about 131 mV. This excellent electrochemical performance can be attributed to the unique structure of N-RGO/MnO. The response of the electrochemical sensor varies linearly with the DA concentrations ranging from 10 μM to 180 μM with a detection limit of 3 μM (S/N = 3). This work is promising to open new possibilities in the study of novel graphene nanostructures and promote its potential electrochemical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...