Red-emission enhancement of the CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphor by partial substitution for Ca3N2 by CaCO3 and excess calcium source addition†
Abstract
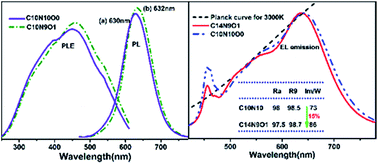
The effects of different calcium sources and the non-stoichiometric calcium addition on the preparation and photoluminescence properties of the red-emitting nitride phosphor CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ were studied. Better crystallinity, enhanced emission intensity, and improved photoluminescence thermal stability of the phosphors were obtained when 10% of the calcium source (Ca3N2) was substituted by CaCO3. The partial substitution for Ca3N2 by CaCO3 resulted in the formation of more transient liquid phases at high temperature, which suppressed the evaporation of Ca/Eu elements to some extent. In order to effectively compensate for the calcium deficiency, excess initial Ca source was added, resulting in a narrower emission band and faster decay rate. Furthermore, the as-synthesized CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ was employed as a red-emitting component to fabricate the two-phosphor-converted white LEDs, which exhibited high color rendering index Ra of ∼98 and warm correlated color temperature of 3000 K, and the narrower emission band with 140% initial Ca content gave an increase of 15% in luminous efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...