Synthesis and application of polypyrrole coated tenorite nanoparticles (PPy@TN) for the removal of the anionic food dye ‘tartrazine’ and divalent metallic ions viz. Pb(ii), Cd(ii), Zn(ii), Co(ii), Mn(ii) from synthetic wastewater†
Abstract
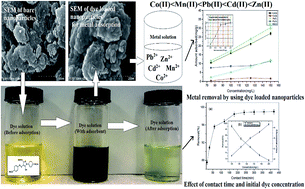
The present study deals with the synthesis of polypyrrole coated tenorite nanoparticles. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by XRD, TEM, SEM and EDS. TEM images showed the formation of nanoparticles with 26–30 nm diameter. The BET surface area of the nanoparticles was determined to be 425 m2 g−1 while the pore diameter of the nanoparticles was found to be 3.57 nm which showed the formation of mesoporous nanoparticles. The pHzpc of the nanoparticles was determined to be 4.4. The removal efficiency of the synthesized nanoparticles for an anionic food dye ‘tartrazine’ was investigated. Decreased removal was observed, when the dye concentration was increased from 100 to 200 mg L−1. It was observed that an acidic medium was favorable for tartrazine removal. A thermodynamic study suggested the endothermic nature of tartrazine adsorption. The value of Ea for the present system was found to be 26.97 kJ mol−1. The best suitable kinetic model was well explained by the pseudo second order model. Langmuir adsorption capacity was measured to be 42.50 mg g−1. Exhausted (dye loaded) nanoparticles were used as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of divalent metallic ions viz. Pb(II), Cd(II), Co(II), Mn(II), Zn(II) and were found to be efficient for the removal of metallic species from a single solute system as well as a multi-solute system. This study reveals that polypyrrole coated tenorite nanoparticles are very efficient for dye removal and the dye loaded exhausted adsorbent is equally good for metal removal because tartrazine loading on nanoparticles makes the surface suitable for metal interaction. Thus, the synthesized nanoparticles prove to be a good candidate for the treatment of dye and metal bearing wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...