Preparation and pyrolysis characteristics of PNIPAM-grafted SiO2 hollow spheres loading vitamin C
Abstract
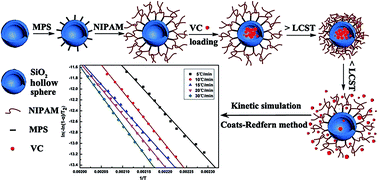
Thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-grafted SiO2 hollow spheres (PSHS) were successfully prepared by a multi-step reaction, and then they were used to load vitamin C (VC). Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of PSHS loading VC were measured via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Two peaks at 193.03 °C and 247.56 °C were obtained in the DTG curve of PSHS loading VC, which corresponded to the decomposition of the physically absorbed VC and bound VC molecules formed by hydrogen bonding between VC and PSHS respectively. The average value of activation energy calculated by the Coats–Redfern method was 78.91 kJ mol−1, equal to the activation enthalpy (77.31 kJ mol−1). The activation entropy was −82.60 J mol−1 K−1 and the activation free energy was 115.82 kJ mol−1. These results proved that VC was encapsulated into PSHS via hydrogen bonding and van der Waals force. Finally, PSHS loading VC exhibited excellent temperature-controllable release property.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...