Detection of pesticide residues on fruit surfaces using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
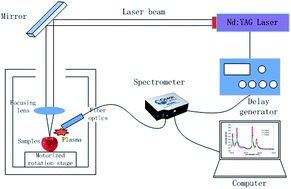
The detection of pesticide residues on fruit surfaces is highly relevant to people’s lives. Based on our previous research, we further explored the detection of chlorpyrifos residues on apple surfaces by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) in this paper. We observed the characteristic peaks of P at 213.62 nm, 214.91 nm, 253.56 nm, and 255.33 nm and the characteristic peak of Cl at 837.59 nm. We studied the influence of pesticide concentration and argon on the intensity of the LIBS signals. The intensity of the LIBS signal showed a linear relationship with the pesticide concentration, and argon could enhance the intensity of the LIBS signal. In the case of purging with argon, the characteristic peak of P was observed in the LIBS spectrum of a chlorpyrifos solution of 1 : 1000 dilution. Then we studied the differences in the LIBS signals of pesticide residues among different matrixes and pesticides. Finally, we performed the quantitative detection of the pesticide residues with LIBS, which will provide a reference for quantitative detection. Our work gives a new method for the fast detection of pesticide residues on fruit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...