Thermal degradation kinetics of nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid and catechin derived from Averrhoa bilimbi fruits†
Abstract
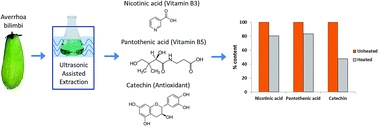
Averrhoa bilimbi fruits contain appreciable amounts of polyphenolic compounds such as nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid and catechin, which can be recovered for use as food supplements. The recovery process of these polyphenols is often accomplished at slightly elevated temperatures, thus it is vital to understand the loss in polyphenolics due to thermal degradation before the mitigating method can be formulated. The thermal degradation kinetics of nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid and catechin derived from Averrhoa bilimbi fruits were investigated at temperatures ranging from 90 to 120 °C and analysed using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results showed nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid and catechin degradation followed the first-order kinetics model. Pantothenic acid showed the lowest degradation rate constant, followed by nicotinic acid and catechin for all studied temperatures, indicating the slowest degradation. The thermal degradation activation energies of nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid and catechin were 43.85 kJ mol−1, 58.86 kJ mol−1, and 21.27 kJ mol−1, respectively. Pantothenic acid has the highest activation energy which implies that the compound is more sensitive to temperature change.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...