Biocompatible degradable injectable hydrogels from methacrylated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(xylitol sebacate) and cyclodextrins for release of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs
Abstract
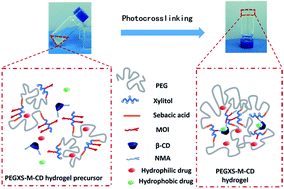
A drug delivery system (DDS) which can achieve a sustained release of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs is highly beneficial for biomedical applications. In this study, we present an injectable photocurable composite hydrogel based on methacrylated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(xylitol sebacate) (PEGXS-M) and acrylamidomethyl-β-cyclodextrin (β-CD-NMA) for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug release. The PEGXS-M copolymers were synthesized by the polycondensation of PEG, xylitol and sebacate, and then incorporation of a methacrylate group. The PEGXS-M-CD composite hydrogels were prepared by the photocrosslinking of a PEGXS-M and β-CD-NMA mixed solution under UV irradiation, and the swelling ratio, rheological properties and degradation behavior of the hydrogels were investigated. The incorporation of β-CD-NMA into the PEGXS-M hydrogel decreased the swelling ratio and meanwhile improved the mechanical properties. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) were cultured in the presence of hydrogels and the cultivation results indicated good biocompatibility of these hydrogels. Furthermore, theophylline and phenethyl alcohol were chosen as hydrophilic and hydrophobic model drugs to be encapsulated within PEGXS-M-CD hydrogels for drug release investigation. The good sustained drug release efficiency of these hydrogels has been successfully confirmed, and the addition of adamantanamine hydrochloride enhanced the release of drugs from the hydrogels. These results suggest that the PEGXS-M-CD composite hydrogels have a great potential in drug delivery for the sustained release of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...